CHARGING
charge up and go
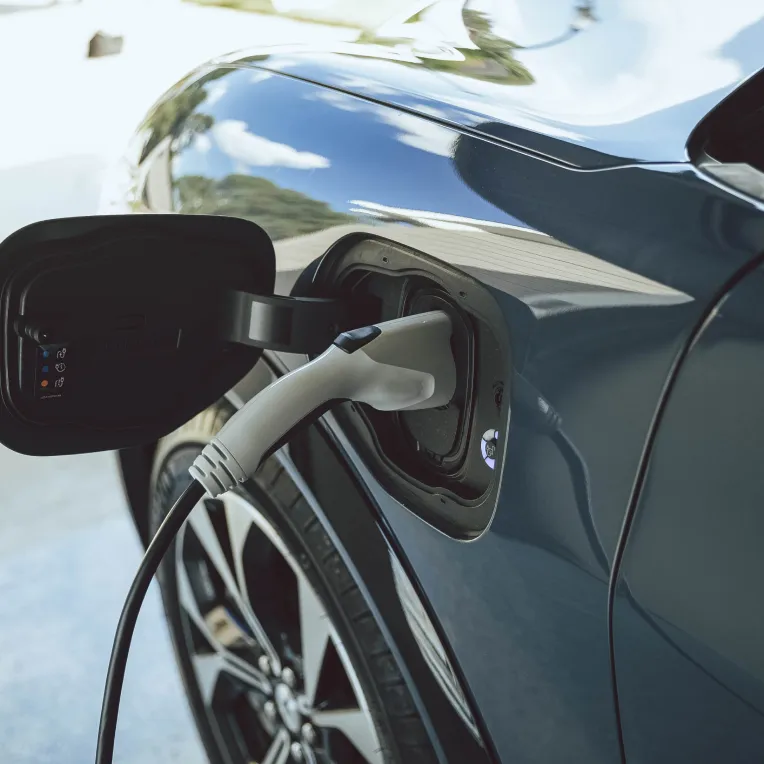
Charging an electric vehicle is as easy as charging your phone or tablet. Unlike gas-powered vehicles, EVs can be “refueled” in several ways and in many different places, including right at home. And with charging station infrastructure improving every day, you’ll one day be able to charge up almost anywhere you park your car.
How to Charge
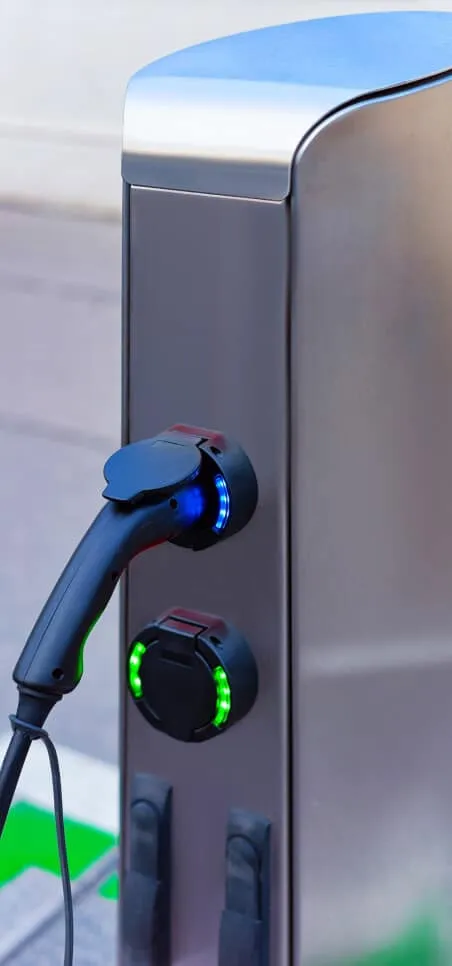
Charging is simple—you already do it every day with other electronic devices, and it works the same way on an EV. Instead of a gas cap and gas tank, EVs have charging ports where you plug in a charger to let the battery power up. You can even charge up overnight when your vehicle is parked at home, so you can get out and go the next day with a fully charged battery.
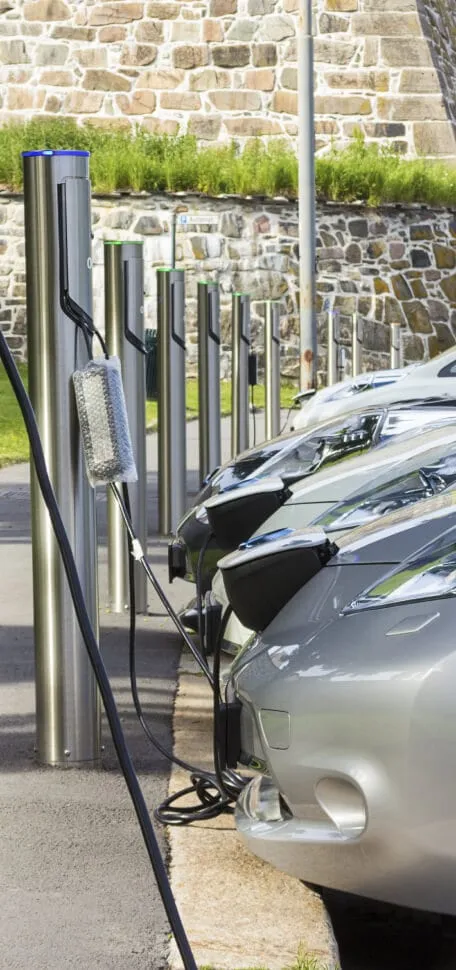
Types of Chargers
There are a few different types of EV chargers with varying power levels. All three types can be found at different public charging stations, but some are better for at-home charging than others. Get familiar with each kind and where you can use them below.

LEVEL 1
Level 1 chargers provide 1 kilowatt of power and take the longest to fully charge your EV battery, so they are perfect for overnight charging at home.

LEVEL 2
Level 2 chargers provide between 3 and 20 kilowatts of power (usually 6 kW) and take about 5 hours to charge your EV battery enough to cover 124 miles. Level 2 chargers also work great at home.
LEVEL 3 (DCFC)
Level 3 (DCFC) chargers are most commonly found at charging stations along highways, so look for these on road trips. They’re the fastest type of charger, taking about 30 minutes to recharge your battery.





Infrastructure Plan
The Alabama Department of Economic and Community Affairs (ADECA) engaged with the Alabama Clean Fuels Coalition (ACFC) to develop a strategy to use funds allocated to EV-related infrastructure planning.
About the Strategy
The strategy is focused on identifying what infrastructure priorities will help drive electric vehicle adoption and emissions reductions in Alabama. Infrastructure planning includes, but is not limited to, the following considerations:
- NOx reduction
- FHWA alternative fuel corridor designation
- Corridors to support interstate commerce
- Corridors to facilitate and grow the EV industry in Alabama
- Commuter patterns and workplace charging
- Multi-family dwelling charging infrastructure
- Traffic density and frequency on corridors
Learn more about Infrastructure Planning
A complete outline of the current plans, including available funds and order of prioritization, is available through ADECA.
Download Plan
